The Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Microbiome Influences Mental Health
Introduction
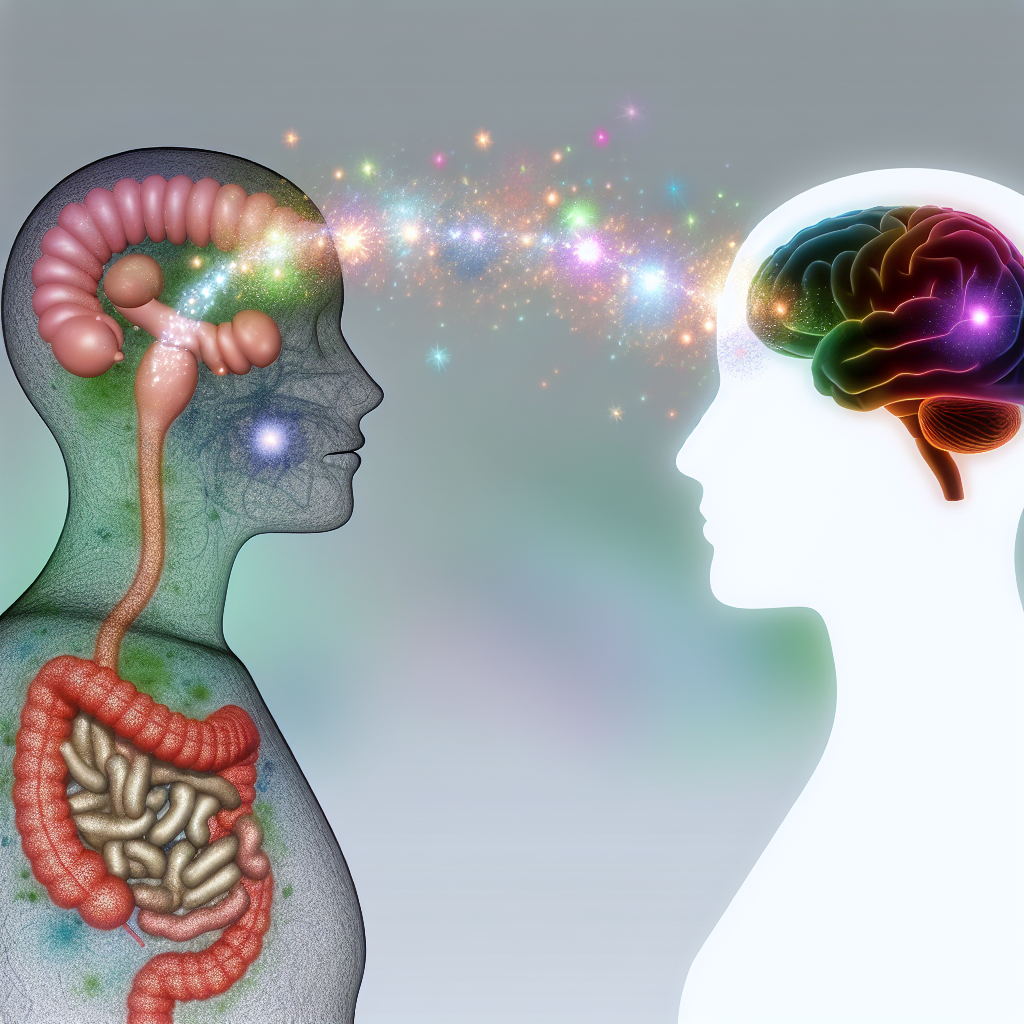
The relationship between the gut and the brain is one of the most fascinating and complex aspects of human physiology. Known as the gut-brain axis, this bidirectional communication system links the central nervous system (CNS) with the enteric nervous system (ENS), profoundly impacting mental and emotional well-being. Recent research suggests that the trillions of microorganisms residing in the gut—collectively known as the gut microbiome—play a crucial role in brain function, mood regulation, and neurological health.
For decades, mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression were primarily attributed to chemical imbalances in the brain. While neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine remain central to these discussions, emerging evidence indicates that the gut microbiome significantly influences their production. In fact, approximately 90% of serotonin—the neurotransmitter often associated with happiness and well-being—is produced in the gut, highlighting the vital connection between digestive health and emotional stability.
Beyond neurotransman1er production, the gut microbiome also regulates inflammation and immune function, both of which have been implicated in mental health disorders. Chronic gut inflammation has been linked to conditions such as major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, and even neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, can lead to systemic inflammation that adversely affects brain function.
Several natural and herbal interventions have been explored to support a healthier gut-brain connection. Herbs such as turmeric, ginger, peppermint, and ashwagandha have been shown to reduce gut inflammation and enhance mental clarity. Additionally, probiotic-rich foods like kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha help replenish beneficial bacteria that support optimal digestion and emotional resilience.
A well-balanced microbiome is becoming increasingly recognized as essential for holistic mental health. By fostering a healthy gut environment through proper diet, lifestyle choices, and natural remedies, individuals may significantly reduce symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression. In this article, we will explore relevant scientific findings on the gut-brain connection and discuss how natural remedies can support both mental and digestive well-being.
The Science Behind the Gut-Brain Axis
A growing body of research underscores the crucial link between gut microbiota and brain function. One of the most groundbreaking studies was conducted by Cryan & Dinan (2012), which introduced the term “psychobiotics” to describe probiotic strains that positively influence mental health. Their research demonstrated that specific probiotics, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like properties by modulating neurotransmitter levels in the brain ([Cryan & Dinan, 2012](https://www.nature.com/articles/nrn3346)).
Further studies highlight how gut bacteria influence stress response. A 2013 study published in *Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences* found that germ-free mice—mice raised without any gut bacteria—exhibited heightened stress and abnormal brain development. When these mice were reintroduced to probiotics, their stress responses normalized ([Sudo et al., 2004](https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.1220901110)). This suggests that early microbial colonization is crucial for developing a balanced stress response later in life.
How Inflammation and Mental Health Are Connected
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in mental health. A 2020 review in *Frontiers in Neuroscience* linked gut inflammation with neuroinflammatory responses, which contribute to mood disorders such as anxiety and depression ([Bauer & Teixeira, 2020](https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.00206/full)). Chronic gut inflammation can lead to neuroinflammation, disrupting brain function and emotional regulation.
To counter inflammation, researchers have explored anti-inflammatory dietary strategies such as introducing polyphenol-rich herbs and probiotic supplements to reduce gut inflammation and support cognitive function.
Herbs and Natural Supplements for a Healthier Gut-Brain Connection
Herbs and natural supplements are now being studied for their potential to support the gut-brain axis. Here are some scientifically supported options:
– Ashwagandha – This adaptogenic herb has been shown to lower cortisol levels (a key stress hormone) while also positively influencing gut bacteria ([Chandrasekhar et al., 2012](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3573577/)).
– Turmeric (Curcumin) – Known for its powerful anti-inflammatory effects, turmeric has been shown to benefit both gut health and brain function ([Lopresti et al., 2015](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165032715000451)).
– Ginger – Helps in reducing gut inflammation and promoting digestion.
– Peppermint – Can soothe the digestive tract and alleviate symptoms of gut irritation.
Probiotics and Fermented Foods: A Natural Boost for Brain Health
Probiotics—beneficial bacteria that populate the gut—play a crucial role in mental well-being. Research has shown that consuming probiotic-rich foods can reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. A 2016 study published in *Gastroenterology* found that women who consumed a probiotic-rich diet exhibited lower activity in brain regions associated with stress and anxiety ([Tillisch et al., 2013](https://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(13)00292-8/fulltext)).
Some of the best probiotic-rich foods to include in your diet are:
– Kefir
– Yogurt (with live cultures)
– Sauerkraut
– Kimchi
– Kombucha
By regularly consuming these foods, individuals can support a diverse and healthy gut microbiome—enhancing both digestive and mental well-being.
Final Thoughts: Prioritizing Gut Health for Mental Well-Being
The gut-brain axis illustrates the profound impact of gut microbiota on neurological health. Scientific research continues to uncover the extensive ways in which gut bacteria influence mood regulation, cognitive function, and mental resilience. Chronic inflammation, stress, and poor diet have been shown to disrupt the microbiome, contributing to anxiety, depression, and even neurodegenerative diseases. However, natural interventions—including probiotic supplementation, fermented foods, and anti-inflammatory herbs such as turmeric and ashwagandha—offer promising strategies for fostering mental well-being through gut health.
A holistic approach to mental and digestive wellness recognizes the importance of a diverse microbiome. By implementing dietary and lifestyle practices that support gut health, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving not only their digestion but also their emotional and cognitive well-being. As research continues to evolve, leveraging the power of the gut-brain connection may offer innovative solutions for managing mental health naturally.
**Summary:**
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that links the gut microbiome with the central nervous system, profoundly impacting mental and emotional well-being. Research shows that the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters, inflammation, and stress response, which are all closely linked to mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. By incorporating natural remedies like probiotics, fermented foods, and anti-inflammatory herbs, individuals can support a healthier gut-brain connection and improve overall mental well-being.
**References:**
– [Cryan & Dinan, 2012](https://www.nature.com/articles/nrn3346)
– [Sudo et al., 2004](https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.1220901110)
– [Bauer & Teixeira, 2020](https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.00206/full)
– [Chandrasekhar et al., 2012](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3573577/)
– [Lopresti et al., 2015](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165032715000451)
– [Tillisch et al., 2013](https://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(13)00292-8/fulltext)

Dominic E. is a passionate filmmaker navigating the exciting intersection of art and science. By day, he delves into the complexities of the human body as a full-time medical writer, meticulously translating intricate medical concepts into accessible and engaging narratives. By night, he explores the boundless realm of cinematic storytelling, crafting narratives that evoke emotion and challenge perspectives.
Film Student and Full-time Medical Writer for ContentVendor.com