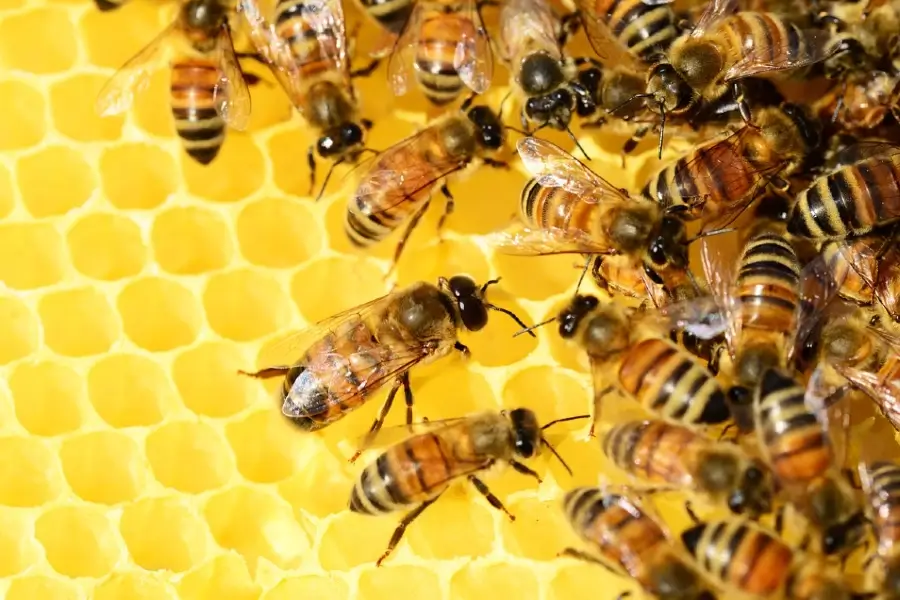
Is honey considered a prebiotic? Indeed, honey can be classified as a prebiotic. Prebiotics refer to food components that cannot be digested by the body and instead serve as nourishment for the good bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. Honey contains a diverse range of oligosaccharides, a specific prebiotic form.
Research has demonstrated that honey can enhance the proliferation of advantageous microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria. These bacteria significantly impact the health of the digestive system and have been associated with several health advantages, including enhanced digestion, strengthened immune system, and decreased inflammation.
Honey has been used as a traditional medicinal treatment for ages due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory characteristics. Recent research has demonstrated that honey can stimulate the proliferation of beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract, vital in maintaining optimal gut health.
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria are the predominant strains of beneficial bacteria commonly present in honey.
Bifidobacteria is a helpful form of bacteria found in honey.
Lactobacillus is a prevalent bacterium in the human gut crucial in producing lactic acid. This acid facilitates the formation of an acidic milieu in the gastrointestinal tract, hence impeding the proliferation of detrimental microbes.
Lactobacillus has demonstrated the ability to enhance digestion and alleviate symptoms associated with digestive illnesses, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Bifidobacteria is a helpful form of bacteria found in honey. Its primary location is within the large intestine, which plays a crucial role in synthesizing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are vital for maintaining gastrointestinal well-being.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) have been associated with many health advantages, such as enhanced immune function, decreased inflammation, and a reduced likelihood of developing chronic conditions, including diabetes and heart disease. Honey stimulates the proliferation of advantageous bacteria and contains prebiotics, a dietary fiber that nourishes these bacteria.
Aside from its prebiotic properties, honey also possesses various other health advantages.
Prebiotics are crucial for preserving a healthy gut microbiome. They promote the proliferation of advantageous bacteria while impeding the growth of detrimental bacteria.
Incorporating honey into your diet can benefit your gut health and overall state of being. Honey can enhance digestion, strengthen immunity, and diminish by stimulating the proliferation of good bacteria and supplying prebiotics.
Aside from its prebiotic properties, honey also possesses various other health advantages. It is a reliable source of antioxidants and has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and antibacterial characteristics. In addition, honey can be utilized to alleviate a sore throat and cough.
Although honey is a nutritious food, it is crucial to consume it in moderation. Honey contains a significant amount of sugar so that excessive use might result in weight gain and other health issues.
If you seek a natural method to enhance your gut health, honey could be a favorable choice.
Here are some suggestions for integrating honey into your dietary routine:
Incorporate a single tablespoon of honey into your tea or coffee.
Apply a thin, gentle stream of honey onto yogurt, cereal, or fruit.
Utilize honey as a natural sweetening agent in baking or cooking.
Include honey in marinades or sauces.
Indulge in honey as a standalone treat.
If you seek a natural method to enhance your gut health, honey could be a favorable choice.

Dominic E. is a passionate filmmaker navigating the exciting intersection of art and science. By day, he delves into the complexities of the human body as a full-time medical writer, meticulously translating intricate medical concepts into accessible and engaging narratives. By night, he explores the boundless realm of cinematic storytelling, crafting narratives that evoke emotion and challenge perspectives.
Film Student and Full-time Medical Writer for ContentVendor.com