The leaky gut diet is a dietary strategy to enhance gut health by fostering the proliferation of good gut bacteria and diminishing inflammation in the digestive tract.
It is crucial to acknowledge that leaky gut syndrome is not a well-defined medical diagnosis but a hypothesis aimed at elucidating various digestive problems. The leaky gut diet is not well-supported by scientific evidence. However, it typically focuses on the following:
Recommended food items:
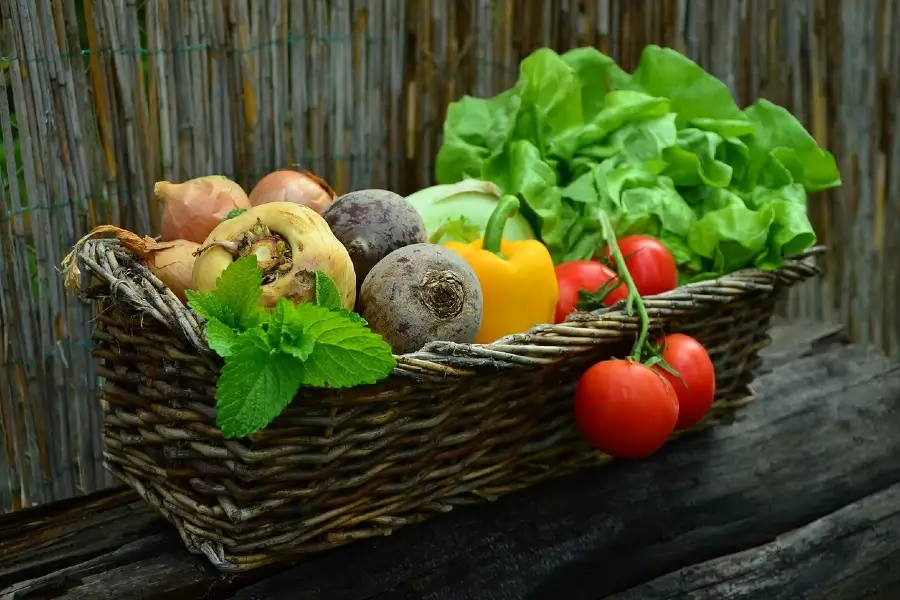
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts are all abundant in fiber, a nutrient that supports the growth of friendly gut flora and aids in maintaining regular bowel movements.
Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha, are rich in probiotics, which are live bacteria that promote a healthy gut microbiome.
Bone broth is a rich source of readily assimilated nutrients and potentially possesses anti-inflammatory qualities.
Lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, and lentils offer vital nutrients that support gut health.
Lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, and lentils offer vital nutrients that support gut health and restoration.
Include unsaturated fats from sources such as olive oil, avocados, and almonds in your diet to promote gut health and enhance overall well-being.
Avoidance of Certain Foods:
Processed foods typically contain elevated levels of refined carbohydrates, harmful fats, and artificial chemicals, which can potentially disturb the balance of microorganisms in the stomach, known as the gut microbiome.
Gluten: For individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, it is imperative to avoid gluten. While some individuals may choose to incorporate gluten elimination in their leaky gut diet, the overall effectiveness of this approach is not uniformly confirmed.
Traditional dairy: Certain individuals may experience difficulty digesting dairy products, and the leaky gut diet may suggest abstaining from them or selecting lactose-free substitutes.
Sugar and processed carbohydrates can nourish harmful gut bacteria and exacerbate inflammation.
Alcohol: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol can disturb the balance of microorganisms in the stomach and increase the permeability of the gut.
Before commencing the leaky gut diet, it is crucial to seek guidance from a medical professional.
Overall Suggestions:
The fundamental idea of the leaky gut diet is to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, which entails consuming a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Consume meals and snacks consistently and attentively: Strive for well-rounded and proportionate food choices throughout the day to promote optimal gut health and facilitate digestion.
Address stress: Prolonged stress can adversely affect the digestive system. Therefore, stress management practices such as yoga or meditation are advisable.
Hydration: Sufficient water consumption is essential for general well-being and can positively impact digestion.
Before commencing the leaky gut diet, it is crucial to seek guidance from a medical professional or certified dietician. They can assist in assessing the product’s suitability for your specific requirements and developing a customized strategy that tackles any underlying medical concerns.
In addition, they can guide the utilization of probiotics and other supplements, given the scarcity of information regarding their efficacy in the context of a leaky gut.

Dominic E. is a passionate filmmaker navigating the exciting intersection of art and science. By day, he delves into the complexities of the human body as a full-time medical writer, meticulously translating intricate medical concepts into accessible and engaging narratives. By night, he explores the boundless realm of cinematic storytelling, crafting narratives that evoke emotion and challenge perspectives.
Film Student and Full-time Medical Writer for ContentVendor.com